Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) are integral to India’s economic framework, significantly contributing to the nation’s GDP, employment, exports, and fostering regional development. Their role is pivotal in driving innovation, entrepreneurship, and inclusive growth across the country.
Understanding MSMEs

Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) play a vital role in shaping India’s economic landscape. Contributing nearly 30% to the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP), this sector serves as a powerful engine for growth and development. With more than 110 million people employed across over 63 million units nationwide, MSMEs are a key driver of job creation and inclusive development.
MSMEs also have a strong presence in India’s global trade. They contribute to approximately 45% of the country’s total exports, highlighting their significance in strengthening India’s export economy. Their widespread geographic distribution supports balanced regional development, bridging the urban-rural divide and stimulating industrialization in underdeveloped areas.
Beyond their economic footprint, MSMEs are often at the forefront of innovation and entrepreneurship. They rapidly adopt emerging technologies and modern business practices, making them agile and adaptable players in a dynamic market. This innovative spirit helps catalyze industrial transformation and fuels grassroots entrepreneurship.
Recognizing the strategic importance of the MSME sector, the Indian government has introduced several supportive initiatives, including a revamped Credit Guarantee Scheme and an increase in the MUDRA loan limit, to enhance financial access and promote business growth.
As India aspires to become a $5 trillion economy, the sustained development and empowerment of MSMEs will be crucial. Their continued progress will not only drive economic expansion but also ensure inclusive and sustainable growth across the nation.
Contribution to GDP

The MSME sector consistently contributes around 30% to India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). According to the Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation, the share of MSME Gross Value Added (GVA) in all India GDP was 30.1% in 2022-23.
Employment Generation

Export Performance

The MSME sector plays a crucial role in India’s exports, contributing significantly to the country’s total exports. According to Directorate General of Commercial Intelligence and Statistics (DGCIS), MSMEs accounted for approximately 45.79% of India’s total exports in the financial year 2024-25. This highlights their capacity to produce goods and services that meet international standards.
Regional Development and Inclusive Growth
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) significantly contribute to regional development and inclusive growth by promoting entrepreneurship beyond major urban centers. They help reduce regional disparities by creating employment opportunities in rural and semi-urban areas, thereby curbing migration to cities and supporting local economies. By utilizing local resources and skills, MSMEs encourage the development of traditional industries and foster self-reliance within communities. Their presence stimulates the growth of infrastructure, such as transportation, banking, and communication services, which further enhances regional development. MSMEs also provide livelihood opportunities to marginalized groups, including women and the youth, promoting social inclusion and economic equity. As a result, they play a vital role in distributing the benefits of economic progress more evenly across regions, contributing to a more balanced and inclusive national growth model.
Innovation and Competitiveness
MSMEs play a critical role in driving innovation due to their inherent agility and responsiveness to market trends. Unlike larger corporations, MSMEs can swiftly pivot their strategies, adopt emerging technologies, and introduce niche products tailored to evolving consumer demands. This adaptability fosters a culture of experimentation and continuous improvement, enabling them to stay ahead in competitive markets. Their innovative approaches not only strengthen their domestic presence but also enhance their appeal in global value chains, contributing to economic resilience and growth.
Government Initiatives Supporting MSMEs in India
Recognizing the critical role that Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) play in driving economic growth, employment, and innovation, the Government of India has implemented several policy measures and schemes to enhance their competitiveness, improve access to finance, and support modernization. Below are some of the key initiatives as of 2025:
1. Mutual Credit Guarantee Scheme (MCGS) – Launched January 2025
Objective:
To ease access to collateral-free credit for MSMEs and reduce lending risks for financial institutions.
Key Features:
- Offers 60% guarantee coverage to Member Lending Institutions (MLIs) for credit facilities.
- Applicable to loans of up to ₹100 crore sanctioned to eligible MSMEs.
- Aims to enhance credit flow to small businesses, especially first-time borrowers and enterprises with limited asset bases.
- Particularly helpful for manufacturing and service-based MSMEs expanding post-COVID and during the global supply chain rebalancing.
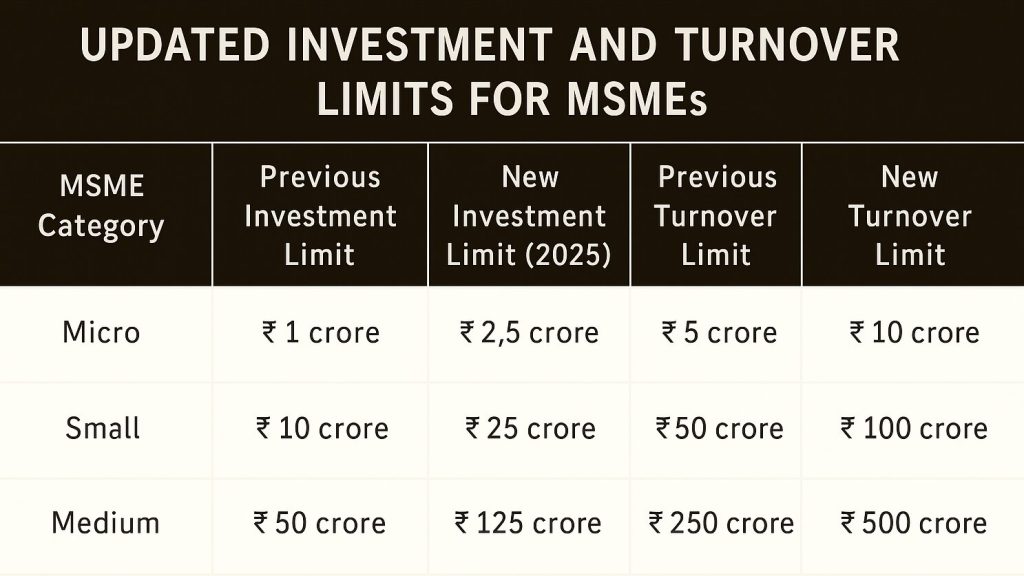
2. Revised Investment and Turnover Limits (Union Budget 2025)
Objective:
To bring more enterprises under the MSME umbrella and incentivize business scaling without loss of MSME benefits.
Revised Limits (as per Budget 2025):
- Investment Limits: Increased by 2.5 times for micro, small, and medium categories.
- Turnover Thresholds: Doubled across all three categories.
3. Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme – Extension to MSMEs in Textile Sector
Objective:
To boost manufacturing and exports of value-added garments and technical textiles by incentivizing MSMEs.
New Policy Highlights:
- Expansion of the PLI scheme to include small and medium textile firms.
- Focuses on high-value products like sportswear, functional clothing, and sustainable textiles.
- Incentive-based on incremental production and exports, helping MSMEs compete globally.
- Targets $50 billion in garment exports by 2030, creating massive employment, especially in rural areas.
4. Other Noteworthy Initiatives (Ongoing & Updated in 2025)
✅ Udyam Registration Portal
- Single-window portal for hassle-free MSME registration.
- Integrated with PAN and GST databases for auto-population and verification.
- Facilitates access to all government schemes and credit support.
✅ Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) – Continued Support
- Extended to cover additional sectors like tourism, hospitality, and retail MSMEs.
- Focus on stressed enterprises seeking revival post-pandemic.
✅ Skill India & Digital MSME
- Promotes digital literacy, tech adoption, and e-commerce onboarding for small enterprises.
- Special training modules for MSMEs on AI, cloud, and export compliance.
Challenges Faced by MSMEs
Despite their significant contributions, MSMEs face several challenges:
- Access to Finance: Many MSMEs struggle to obtain timely and adequate financing, hindering their growth and expansion plans. Traditional banking institutions often perceive them as high-risk due to limited collateral and credit history.
- Technological Upgradation: Limited resources often prevent MSMEs from adopting advanced technologies, affecting their productivity and competitiveness.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex regulatory frameworks can be burdensome for small enterprises, diverting their focus from core business activities.
The Road Ahead
To further strengthen the MSME sector, concerted efforts are required from all stakeholders:
- Enhanced Financial Support: Financial institutions should develop tailored products to meet the unique needs of MSMEs, ensuring easier access to credit.
- Skill Development Programs: Implementing training programs can equip the workforce with necessary skills, enhancing productivity and innovation within MSMEs.
- Infrastructure Development: Improving infrastructure, such as transportation and digital connectivity, can facilitate smoother operations and market access for MSMEs.
- Simplified Regulatory Processes: Streamlining compliance procedures can reduce the administrative burden on MSMEs, allowing them to focus on growth and development.
In conclusion, MSMEs are indeed the backbone of the Indian economy. Their contributions to GDP, employment, exports, and regional development underscore their critical role. By addressing existing challenges and leveraging government initiatives, MSMEs can propel India towards greater economic prosperity and global competitiveness.
Case Studies: Success Stories in India
1. Jaipur Rugs – Empowering Rural Artisans
- Founder: Nand Kishore Chaudhary
- Headquarters: Jaipur, Rajasthan
- Industry: Handwoven carpets and rugs
- Impact: Over 40,000 artisans across 600 villages
Story:
Jaipur Rugs started in 1978 with just two looms and a vision to bridge the gap between rural artisans and global markets. Today, it exports handcrafted rugs to over 60 countries. It has empowered thousands of women weavers, provided fair wages, and preserved dying art forms.
2. Ather Energy – From Startup to Electric Mobility Pioneer
- Founders: Tarun Mehta & Swapnil Jain
- Headquarters: Bengaluru, Karnataka
- Industry: Electric Vehicles (EV)
- Support: Seed funding from IIT Madras, later backed by Flipkart founders
Story:
Started as a college project, Ather Energy now produces some of India’s most innovative electric scooters like Ather 450X. Despite stiff competition from giants like Ola Electric and Bajaj, it has carved out a niche with its design, IoT integration, and battery innovations.
3. Vini Cosmetics – The Brand Behind Fogg
- Founder: Darshan Patel
- Headquarters: Ahmedabad, Gujarat
- Industry: FMCG (Personal Care)
Story:
After leaving Paras Pharma, Darshan Patel launched Vini Cosmetics in 2010 with the iconic Fogg deodorant brand. In just a few years, Fogg overtook giants like Axe in the Indian market. Innovative marketing and understanding consumer behavior were key.
4. Agastya International Foundation – Grassroots Innovation in Education
- Founder: Ramji Raghavan
- Headquarters: Bengaluru, Karnataka
- Industry: Education (Non-Profit MSME)
Story:
Started in 1999, Agastya runs mobile science labs and hands-on learning programs for underprivileged children. With over 1,800 employees, it has reached over 15 million children across India, especially in remote areas.
5. ID Fresh Food – Reinventing the Dosa Batter Business
- Founder: PC Musthafa
- Headquarters: Bengaluru, Karnataka
- Industry: Food & Beverages
Story:
Musthafa, son of a daily wager, launched ID Fresh with ₹50,000. The company now delivers fresh dosa, idli batter, and ready-to-cook food to over 45,000 outlets across India and the UAE. A focus on hygiene, automation, and authenticity helped them grow rapidly.
Conclusion
MSMEs are not just participants in India’s economic journey—they are its very foundation. Their contributions to GDP, employment generation, exports, and regional development make them indispensable to the nation’s progress. By driving innovation, empowering entrepreneurs, and uplifting rural and semi-urban areas, MSMEs embody the spirit of self-reliance and inclusive growth. As India charts its path toward becoming a $5 trillion economy, the resilience and vitality of the MSME sector will remain central to achieving this vision. Nurturing and empowering these enterprises is not just an economic imperative—it is a national priority.





